Mitosis : Cell division in body cells (somatic cells)
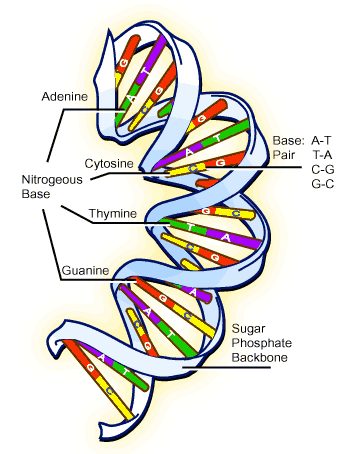
When a cell is not dividing there is not much detailed structure to be seen in the nucleus. Just before cell division, a number of long, thread-like structures appear in the nucleus. These threads are called chromosomes.
Each chromosome is seen to be made up of two parallel strands, called chromatids. When the nucleus divides into two one chromatid from each chromosome goes into each daughter nucleus. The chromatids in each nucleus now become chromosomes and later they will make copies of themselves ready for the next cell division. The process of copying is called replication. It is called replication because it makes the exact copy of itself.
Mitosis has specific function in producing new cells for growth or replacement.
…………………………………………………
Meiosis: Cell division in sex cells(sperm/egg) of reproductive organs.
In a cell which is going to divide and produce gametes, the diploid number of chromosomes shorten and thicken as in mitosis. The pairs of homologous chromosomes, lie alongside each other and when the nucleus divides for the first time. It is the chromosomes and not the chromatids which are separated. This results in only half the total number of chromosomes going to each daughter cell.






 Lock and key model
Lock and key model