What is light???
Light is a type of energy which travels as a wave from a luminous source (eg the Sun, a flame, or a torch). Not everything is a light source. Paper reflects light from a light source towards your eyes, making you able to see it.
Light travels at a speed of 3×108 m/s. Light travels faster than sound which is why you see a flash of lightning before you hear thunder! It takes 8 minutes for light from the Sun to reach Earth.
Light travels in straight lines. It can’t bend itself around objects if they are in its path. Shadows occur where light has been blocked by an object.
………………………………………………………………..
Light reflection
Lots of spectacular and beautiful effects are caused by the reflection of light. Reflections occur when light bounces off the surface of water or some other smooth surface into your eyes.
Reflection from smooth surfaces (eg mirrors or calm water) leads to regular reflection. Bumpy or rough surfaces do not reflect light evenly. The light isscattered in all directions, and usually we cannot see an image. This is known as diffuse reflection.
………………………………………………………………..
Mirror: Light reflection
Light can be made to change direction with mirrors – this is called reflection. When light is reflected off a mirror, the angle at which it hits the mirror (angle of incidence) is the same as the angle at which it is reflected off the mirror (angle of reflection). The rays of light which hit the mirror are called the incident rays; those reflected off the mirror are called the reflected rays. The angles are always measured from the ray to the “normal”. The normal is a line at right angles to the mirror.
The laws of reflection Terms:
- Angle of incidence: The angle between the ray of light that hits the mirror and the normal.
- Angle of reflection: The angle between the ray of light that is reflected off the mirror and the normal.
- Incident ray: The ray shinning onto the mirror.
- Reflected ray: The ray that bounces off the mirror. Normal: A line that is drawn at right angle(90°) to the mirror
………………………………………………………………..
Light reflected from a plane mirror
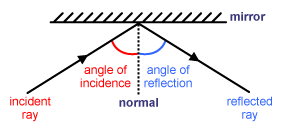
If the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are measured using a protractor then we will always find that
ANGLE OF INCIDENCE = ANGLE OF REFLECTION
………………………………………………………………..
Curved mirrors: Images

- Images in convex mirrors are always smaller & the right way up.
- Uses of convex mirrors: shop-lifting mirror, mirror at a road corner.
- Images in concave mirrors can be: larger and the right way up, if eye is very close to the mirror OR smaller and upside down if eye is away from mirror.
- Uses of concave mirrors: shaving mirror, dentist mirror.
