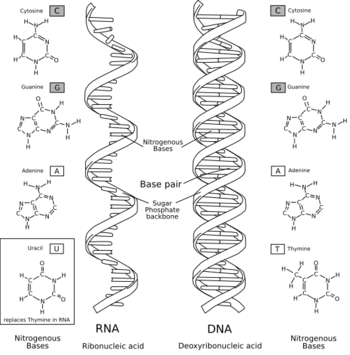
From biological view, evolution of living things could not have occurred without the ability to pass their characteristics from one generation to the next. Chromosomes has its role in transmitting an organism’s hereditary characteristics to its young by means of ‘units of heredity’ called genes.
New species can evolve if creatures become isolated by water, mountains, or other barriers, so can no longer breed with their own kind.
Living things are always exposed to risk from disease, predators, and other dangers. If the young are born with differences that make them tougher, or stronger, or better suited to their surroundings, they will be able to live longer and have more babies than their weaker brothers and sisters.
This idea is called survival of the fittest, or natural selection. Nature selects the fittest and strongest for survival by killing off the weaklings. The idea was first introduced by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace over a hundred years ago.
There are many reasons why some creatures gradually declined in numbers until they became extinct. Climate can change from burning deserts to freezing ice ages, so that, unless living things can migrate to better conditions, or evolve which are in some way better equipped to survive. These take over the living space and food supply of some existing species, depriving them of the necessities of life.
- A criticism of evolution: Evolution is only a theory!?
A scientific definition of evolution is ‘a change in the genes of a population over time’. This leads, for example, to insects developing resistance of pesticides. Evolution in this sense of the word is an indisputable fact. What critics forget is that this mechanism is all that is needed to produce a variety of creatures from a common ancestor and with time, new species.
People who still insist that evolution is ‘only a theory’ imply that it is no more than a tentative suggestion. In fact this ‘theory’ is based on a mass of evidence from fossils, anatomy, ecology, genetics, animal behaviour, and more..