Function of chromosomes
When a cell is not dividing, its chromosomes become very long and thin. Along the length of chromosome is a series of chemical structures called genes. The chemical which forms the genes is called DNA. Each gene controls some part of the chemistry of the cell. It is these genes which provide the instructions. One gene may instruct the cell to make the pigment which is formed in the iris of brown eyes. On one chromosome there will be a gene which causes the cells of the stomach to make the enzyme pepsin. When the chromatids separate at mitosis, each cell will receive a full set of genes. In this way, the chemical instructions in the zygote are passed on to all cells of the body. All the chromosomes, all the instructions are faithfully reproduced by mitosis and passed on complete to all the cells.
………………………………………………….
‘Chromosome’과 ‘DNA’의 의미를 제대로 알고 사용해야한다. Chromosome이란 세포의 핵안에 있는 유전물질(genetic material)을 말한다. DNA는 Deoxyribonucleic Acid의 약자인데… 이것을 생각해보면 분명 화학적 의미를 가지고 있다는걸 알게된다. DNA는 즉, chromosome을 이루고 있는 molecule의 집합이고, nucleic acid/nucleotide 로 이루어져 있다.
(NCEA시험이든 CIE시험이든 이 두단어를 제대로 구분하지 못하고 쓰지 못하면 점수를 획득할수 없다!)
………………………………………………….
Genes
Chromosomes consist of a protein framework, with a long DNA molecule coiled round the framework in a complicated way. Its the DNA part of the chromosome which controls the inherited characters and it is sections of the DNA molecule which constitute the genes. The gene which causes brown eyes will have no effect in a stomach cell and the gene for making pepsin will not function in the cells of the eye.
………………………………………………….
(다시 DNA로 돌아와서..!)
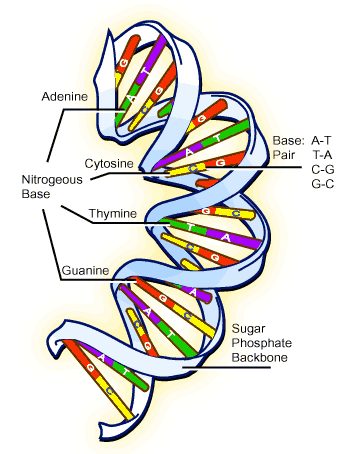
A DNA molecule is a long chain of nucleotides. A nucleotide is a 5 carbon sugar molecule joined to a phosphate group and an organic base.
In DNA, the sugar is Deoxyribose and the organic base is either
- A = adenine
- T = thymine
- C = cytosine
- G = Guanine
The sequence of bases forms a code which instructs the cell to make particular proteins. Proteins are made from amino acids linked together. The type and sequence of the amino acids joined together will determine the kind of protein formed. It is the sequence of bases in the DNA molecule which decides which amino acids are used and in which order they are joined. Each group of three bases stands for one amino acid.
A gene, then, is a sequence of triplets of the four bases, which specifies an entire protein. Most proteins contain a thousand or more bases.
The chemical reaction which take place in a cell determine what sort of a cell it is and what its functions are. These chemical reactions are controlled by enzymes. Enzymes are proteins. Therefore the genetic code of DNA, in determining which proteins, particularly enzymes are produced in a cell, and determines the structure and function of the enzymes.
………………………………………………….
Replication of DNA
(기억할것! Replication은 Mitosis 과정중 일어난다.)
The DNA in a chromosome consists of 2 chains of nucleotides held together by chemical bonds between the bases. The size of the molecule ensures that adenine always pairs with thymine and cytosine pairs with guanine. The double strand is twisted to form a helix.
Before cell division can occur, the DNA of the chromosome has to replicate – to make identical copy of it-self. To do this, enzymes make the double strands of DNA unwind and separate into two single strands rather like undoing a zip.
Nucleotides are brought to the unzipped DNA and joined to the exposed bases with the aid of enzymes. The adenine of an arriving nucleotide always joins to the thymine of the DNA, and cytosine to the guanine.
The new nucleotides join up to form a chain attached to the exposed strand. This happens all the way along each DNA strand. Since this is happening in both strands of DNA strand, the double helix is replicated and the full set of genetic instructions is passed to both daughter cells at cell division.
………………………………………………….
수많은 궁굼증을 해소해야만 이해할수 있는 Gene expression! 공부하면 할수록 어려운 부분이긴 하지만 결코 넘지 못할 산은 아니다.